Unsubscribe
To unsubscribe, please enter your e-mail address below or send us an e-mail at unsubscribeeu@blueprintmedicines.com
Please enter a valid e-mail address
This figure provides a summary of diagnostic considerations for patients with suspected SM, drawn from published recommendations authored by international experts: ECNM User's Guide (Valent 2022 et al.),1 Waters et al. 20222 and Chovanec et al. 2023.3 It is intended as a simplified educational tool and should not be interpreted as a formal diagnostic algorithm; it does not replace the need for a complete evaluation of the patient by a healthcare professional.
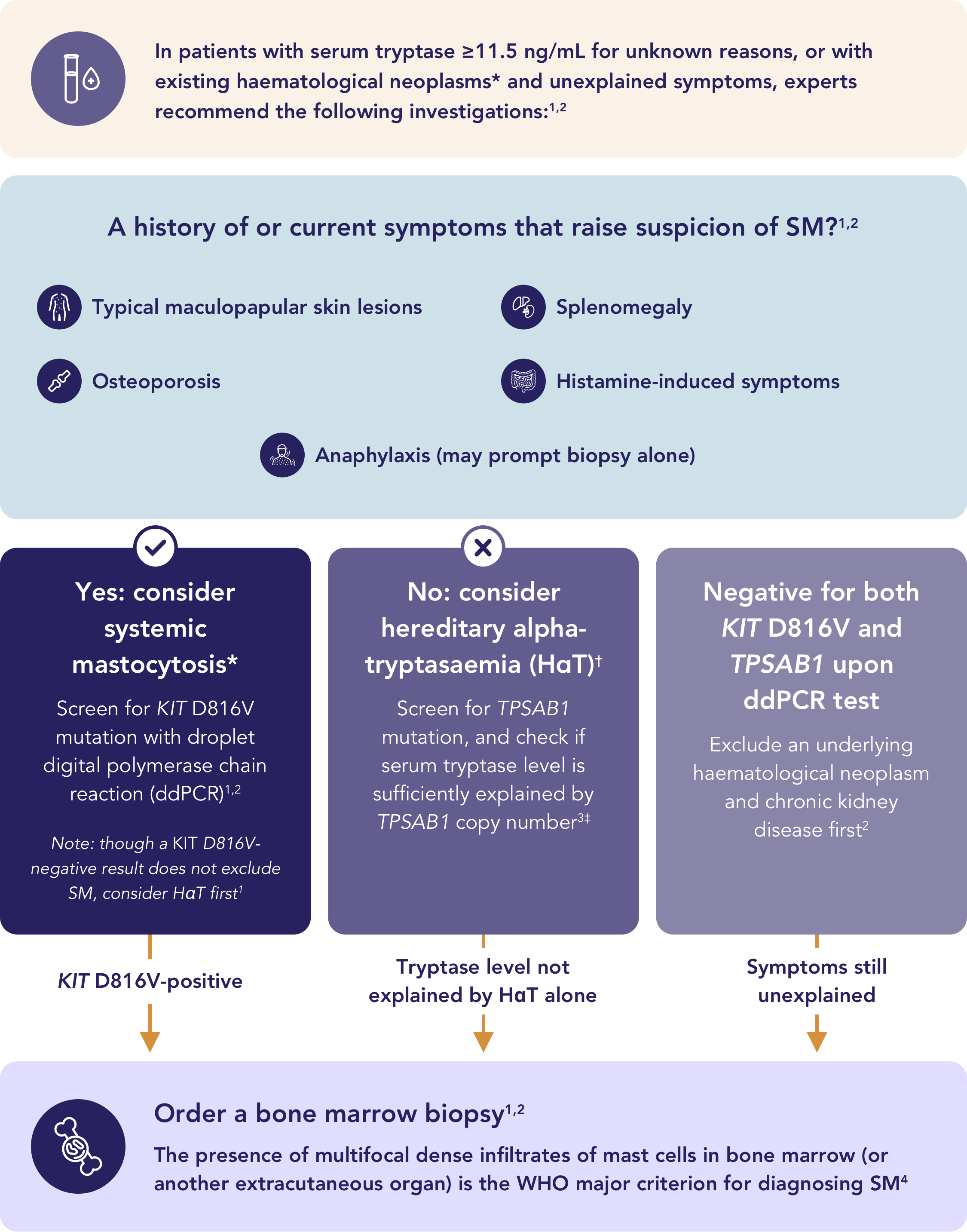
*If there is a clinical suspicion in an existing haematological neoplasm (e.g. allergy) and/or a positive KIT mutation, re-evaluating the bone marrow (typically ordered for the existing haematological neoplasm) can correctly diagnose SM-AHN.5
†HαT is a common genetic trait caused by extra copies of the TPSAB1 gene, leading to elevated basal serum tryptase, found in up to 7% of the population.2,5
‡Reference thresholds for expected BST ULN according to TPSAB1 replication (N): N=0 → 11.4 ng/mL; N=1 → 36.2 ng/mL; N=2 → 62.2 ng/mL; N=3 → 88.8 ng/mL; N=4 → 115.9 ng/mL.3
BST=basal serum tryptase; ddPCR=digital droplet polymerase chain reaction; HαT=hereditary alpha-tryptasaemia; SM-AHN=systemic mastocytosis with an associated haematological neoplasm; ULN=upper limit of normal; WHO=World Health Organization.
Download the diagnostic algorithm leaflet to guide differential diagnosis of SM from common conditions
Order a complete workup to confirm a diagnosis of SM using the WHO criteria1,4
Multifocal dense infiltrates of mast cells (≥15 mast cells in aggregates) in bone marrow biopsies and/or in sections of other extracutaneous organ(s)
If at least 1 major and 1 minor or 3 minor criteria are fulfilled → the diagnosis is SM
*In tissue sections, an abnormal mast cell morphology counts in both a compact infiltrate and a diffuse (or mixed diffuse + compact) mast cell infiltrate. However, the spindle-shaped form does not count as an SM criterion when mast cells are lining vascular cells, fat cells, nerve cells or the endosteal-lining cell layer. In the bone marrow smear, an atypical morphology of mast cells does not count as an SM criterion when mast cells are located in or adjacent to bone marrow particles.
†Any type of KIT mutation counts as a minor SM criterion when published solid evidence for its transforming behaviour is available.
‡All 3 markers fulfil this minor SM criterion when expression in mast cells can be confirmed by either flow cytometry or by immunohistochemistry or by both techniques.
§Although the optimal way of adjustment may still need to be defined, one way is to divide the basal tryptase level by 1 plus the extra copy numbers of the alpha tryptase gene. Example, when the tryptase level is 30 and 2 extra copies of the alpha tryptase gene are found in a patient with HαT, the HαT-corrected tryptase level is 10 (30/3 = 10) and thus is not a minor SM criterion.
Want to learn more about Systemic Mastocytosis?
Visit our Resources Page for more information.
Take me there!